React
React is an open-source JavaScript library that is used for building user interfaces specifically for single-page applications. It's used for handling the view layer for web and mobile apps. It follows the component based approach which helps in building reusable UI components.
Setup React
Pre requisites:
- Node >= 8.10
- npm >= 5.6
- yarn >= 1.22
npx create-react-app my-app
cd my-app
yarn start
Virtual DOM
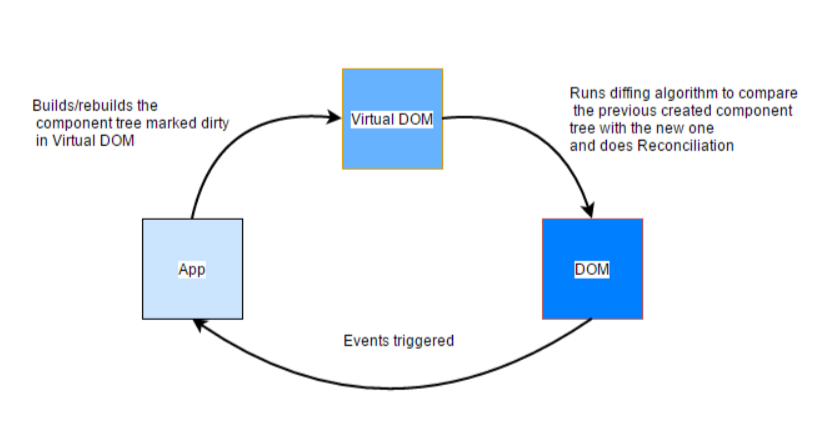
A virtual DOM is a lightweight JavaScript object which originally is just the copy of the real DOM. It is a node tree that lists the elements, their attributes and content as objects and their properties. React’s render function creates a node tree out of the React components. It then updates this tree in response to the mutations in the data model which is caused by various actions done by the user and this is synced with real DOM. This process is called reconciliation.
The VDOM works in 3 main steps:
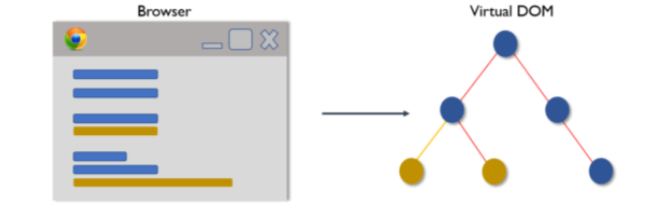
Whenever any underlying data changes, the entire UI is re-rendered in Virtual DOM representation.
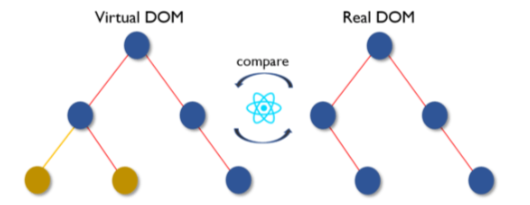
Then the difference between the previous DOM representation and the new one is calculated.
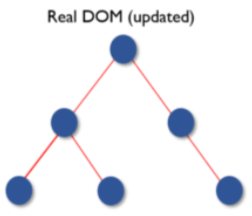
Once the calculations are done, the real DOM will be updated with only the things that have changed.
JSX
- JSX is a shorthand for JavaScript XML.
- This is a type of file used by React which utilizes the expressiveness of JavaScript along with HTML like template syntax.
- While rendering JSX produces React "elements".
const element = 'React Introduction';
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById('root'));
Rendering DOM Elements
A div element present in our index.html file say for e.g.
<div id="root"></div>;
const element = 'React Introduction';
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById('root'));
- The ReactDOM.render function renders a React Element to a DOM Node.
ReactDOM.render(reactElement, domNode), the DOM Node's content will be replaced with the content specified by the React Element. - If the DOM Node already contains content it gets updated to reflect the new React Element as per the diffing algorithm.
Components
Components in React can be a JavaScript class or function that optionally accepts inputs i.e. properties(props) and returns a React element that describes how a section of the UI should appear.
const Greeting = (props) => <h1>Hello {props.name}!</h1>;
The above example shows a functional component that takes props and returns a React Element for rendering. Functional Components are pure components and stateless.
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>Hello {this.props.name}</div>;
}
}
These components are created using ES6’s class syntax. You can use class components if you
- need to manage local state
- need to add lifecycle methods to your component
Understanding State and Props
Props
- Props is the shorthand for Properties in React.
- They are read-only components which must be kept pure i.e. immutable.
- They are always passed down from the parent to the child components throughout the application.
- A child component can never send a prop back to the parent component which helps in maintaining the unidirectional data flow and is generally used to render the dynamically generated data.
State
- States are the objects which determine components rendering and behavior.
- They are mutable unlike the props and create dynamic and interactive components.
- They are accessed via
this.stateand changes viathis.setState().
Events
Handling events with React elements is very similar to handling events on DOM elements with some syntax differences:
- Events are named using camel case instead of lowercase.
- Events are passed as functions instead of strings. The event argument contains a set of properties, which are specific to an event. Each event type contains its own properties and behavior which can be accessed via its event handler only.
<button onClick={activateUsers}>Activate Users</button>
React Router
React Router is a standard library for routing in React. It enables the navigation among views of various components in a React application, allows changing the browser URL and keeps the UI in sync with the URL.
yarn add react-router-dom
The main Components of React Router are:
BrowserRouter: BrowserRouter is a router implementation that uses the HTML5 history API(pushState, replaceState and the popstate event) to keep your UI in sync with the URL. It is the parent component that wraps other components.
Route: Route is the conditionally shown component that renders some UI when its path matches the current URL.
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route exact path='/profile component={Profile}></Route>
- Link: Link component is used to create links to different routes and implement navigation around the application. It works similar to
<a>tag.
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/profile">Profile</Link>
</li>
</ul>
Styling and CSS
CSS Stylesheet
Styling in React can be done by passing className property to component.
import React from 'react';
import './Box.css';
const StyleComponent = () => (
<div className="Box">
<p className="Box_content">Get started with CSS styling in react</p>
</div>
);
export default StyleComponent;
Box.css file
.Box {
margin: 40px;
border: 5px dotted pink;
}
.Box_content {
font-size: 15px;
text-align: center;
}
Inline styling
In React, inline styles are not specified as a string. Instead they are specified with an object whose key is the camelCased version of the style name, and whose value is the style’s value, usually a string.
const divStyle = {
margin: '40px',
border: '5px solid pink',
};
const pStyle = {
fontSize: '15px',
textAlign: 'center',
};
const Box = () => (
<div style={divStyle}>
<p style={pStyle}>Get started with inline style</p>
</div>
);
CSS classes are generally better for performance than inline styles.
Styled-components
Styled-components is a library for React that allows you to use component-level styles in your application that are written with a mixture of JavaScript and CSS
import React from 'react';
import styled from 'styled-components';
const Div = styled.div`
margin: 40px;
border: 5px outset pink;
&:hover {
background-color: yellow;
}
`;
const Paragraph = styled.p`
font-size: 15px;
text-align: center;
`;
const OutsetBox = () => (
<Div>
<Paragraph>Get started with styled-components </Paragraph>
</Div>
);
export default OutsetBox;